In the age of social media and Instagram, people are becoming more and more influenced by the lifestyles they see on social media. This gives a rise to aspirations to attain wealth and live a very comfortable if not a luxurious life. Not everyone is blessed with a good amount of wealth, born in an affluent family or have a high income. It is good to work hard towards your goals and achieve success over time but even though most people want to become wealthy, they just don't get it. We all have seen a prince marrying an ordinary woman in fairy tales. In Korean drama, it is very common to see an extremely rich man marrying an ordinary woman or vice versa. Marrying a rich man/woman can be a shortcut for someone to escape poverty and attain the desired level of wealth and financial freedom. During my consultations, several people come up to me with these questions and through this article I want to guide you to find the best approach for your life based on your planetary placemen...
Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
Definition: Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF) is a type of attack that
occurs when a malicious Web site, email, blog, instant message, or program
causes a user's Web browser to perform an unwanted action on a trusted site for
which the user is currently authenticated.
For example, this attack could result in a transfer of funds,
changing a password, or purchasing an item in the user's context.
Session Id: Long string, randomly generated to identify a logged in
user. Session ids are locked with the IP address of system for which it was
generated (same session id cannot be used on 2 different systems; this is a
simple way through which Session Ids make connections secure). Typically short
lived and expires as soon as user logs out or shuts the system down.
Token Id: Cryptographically secured large random string, generated
once for each session.
Example: When a user logs in to a website, Server issues a
unique Token id (say, ‘abcd1234’). This token id is stored as a hidden field in
the requested html form. Every time user makes a query, the Token id stored in
the form is used to identify the user.
NOTE: Similarity between Token Id and Session Id,
1.
Randomly generated long strings.
2.
Generated when a user logs in.
3.
Remains as long as session continues (or, user is
logged in).
 |
| Fig: Cross Site Request Forgery (CSRF) |
CSRF Attack and
Prevention
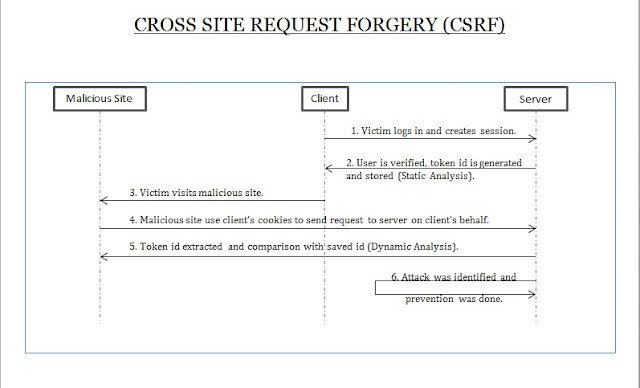
When a user logs in to a website, a session is created and a
token id is generated for that session and stored on the server side (Static
Analysis). Form (web page) requested by the user contains that token id as a
hidden field. When user makes a query, the form is sent along with the token id
present in it, which does the user verification (Dynamic Analysis).
During a CSRF attack, attacker sends the form/query through
the user system. Since the form sent by the attacker does not contain the token
id, therefore verification is failed during dynamic analysis and attack is
identified.
An attacker
can never modify data coming through the server; it can only have access and
send data from the client site.
This diagram
shows that a malicious site is using user/client/victim’s cookies in order to
submit a form and make the CSRF attack happen.
But the
token id is stored in encrypted form in the cookies, which cannot be read or
modified by the attacker. Hence no form submission can be forced and server is
prevented from attack.
Other type of web attack are XSS & SQL Injection.
 |
| CSRF Attack & Prevention Sequence Diagram |
Other type of web attack are XSS & SQL Injection.